As a metal detectorist for over 10 years, I have found many coins in different places and conditions. Some look shiny and new, while others look dull and old.
Some of them look like they have rusted, but is that really possible?
But have you ever wondered if quarters rust? Maybe you found an old jar of coins in your attic and noticed that some of the quarters have a rusty appearance.
Well, the answer is that quarters do not rust, but they can become discolored due to oxidation of the copper and nickel alloy used to make them.
In this article, I will share with you some of the facts and myths about quarters and rust, such as:
- Do quarters rust?
- Which coins can rust?
- What does a rusty quarter look like?
- How do you prevent quarters from rusting?
- How do you clean rusty quarters?
- Do quarters have metal in them?
- Can rusty quarter be worth anything?
You will learn some helpful information and tips on how to identify, clean, and value your coins. So, let’s dive in!
Page Contents
Key Takeaways
- Quarters do not rust but can become discolored due to oxidation of the copper and nickel alloy used to make them.
- A rusty quarter may have a brownish or reddish discoloration on its surface, but this is not actually rust.
- Oxidation is a natural occurrence that happens over time when copper and nickel react with oxygen in the air.
Do Quarters Rust?
Have you ever wondered if quarters rust like other metals? Rust is a type of corrosion that forms on iron or steel when it comes into contact with oxygen and water.
When iron or steel rusts, it creates a reddish-brown coating on the surface, which can be flaky and crumbly.
But what about quarters? Do they rust like iron or steel?
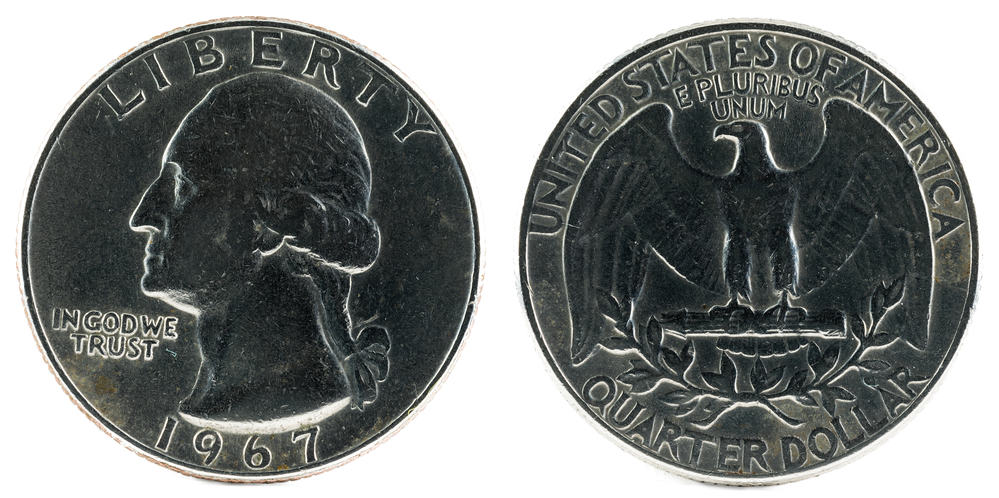

The answer is no. Quarters are made of a copper-nickel alloy, which is non-ferrous and does not contain iron. Therefore, quarters do not rust.
However, over time, quarters can still experience corrosion or tarnish. Corrosion is a general term for the deterioration of metals caused by chemical reactions with the environment.
Tarnish, on the other hand, is a type of corrosion that specifically affects metals like copper and silver.
One common way quarters can corrode is through exposure to moisture and air. This can cause the surface of the quarter to become discolored or develop small spots.
Additionally, if a quarter is exposed to certain chemicals or acids, it can corrode.
In conclusion, quarters do not rust like iron or steel, but they can still corrode or tarnish over time. It’s essential to handle your coins with care and store them properly to prevent damage.
Which Coins Can Rust?
Have you ever wondered if coins can rust? The answer is yes, some coins can rust.
Pennies, nickels, and foreign coins that contain iron are some examples of coins that can rust.
However, quarters are not one of them since they are made of either silver or copper-nickel, which are not ferrous metals that can rust.

The reason why some coins can rust and others cannot depends on their metal composition.
Ferrous metals, such as iron and steel, are prone to rusting because they contain iron that reacts with oxygen and moisture in the air to form iron oxide, also known as rust.
Non-ferrous metals, such as copper, nickel, and silver, do not contain iron and are less likely to rust.
Factors such as moisture, chemicals, or soil can increase the risk of rusting. When coins come into contact with water or other liquids, they can rust more quickly.
Chemicals such as acids or cleaning solutions can also cause rusting by reacting with the metal surface. Soil can also contain moisture and chemicals that can cause rusting over time.
While some coins can rust, quarters are not one of them. The metal composition of a coin determines whether it is prone to rusting.
To prevent rusting, store your coins in a dry and cool place away from moisture and chemicals, and avoid touching them with bare hands.
What Does a Rusty Quarter Look Like?
So, you found a quarter that looks rusty? Well, it’s not actually rust. What you’re seeing is corrosion or tarnish.
A corroded or tarnished quarter can have various signs, such as a change in color, loss of shine, spots, or stains.

The most common colors for a corroded quarter are brown, green, or black. Sometimes, the discoloration can be patchy or spotty, while other times, it can be more uniform.
Loss of shine is also a common sign of corrosion or tarnish. A once-shiny quarter may now appear dull or matte. The surface may also be rough or pitted.
Spots or stains can also be present on a corroded quarter. These can be caused by exposure to various substances, such as water, air, salt, acid, or dirt.
These stains can be difficult to remove and may be permanent.
Sometimes, a quarter may have been improperly stored or exposed to harsh chemicals, which can accelerate the corrosion process.
If you’re a metal detector enthusiast, you may also find that quarters buried underground for long periods can develop corrosion or tarnish.
How to Prevent Quarters from Rusting
As quarters are made of metals like copper, nickel, and silver, they can tarnish or corrode over time due to exposure to air, moisture, and chemicals.
Fortunately, there are several ways to prevent quarters from rusting and keep them looking shiny and new for a long time. Here are some tips to help you:
- Store them properly: One of the best ways to prevent quarters from rusting is to store them in a dry and cool place. Avoid keeping them in damp or humid areas, as moisture can cause oxidation and corrosion. You can also use airtight containers or bags to protect them from air and moisture.
- Avoid contact with chemicals: Quarters can react with chemicals or substances like acids, salts, and oils, which can cause them to tarnish or corrode. So, it’s best to avoid touching them with bare hands or storing them near chemicals. If you need to handle them, wear gloves or use tweezers to avoid contact.
- Clean them regularly: To keep your quarters looking shiny and new, it’s essential to clean them gently with mild soap and water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasives, as they can scratch or damage the surface of the coins. You can also use a soft cloth or brush to scrub the coins and remove any dirt or grime gently.
- Use protective coatings: Another way to prevent quarters from rusting is to use protective coatings or sprays that can prevent oxidation and corrosion. You can find several products in the market that are specifically designed for coins and metals. Make sure to follow the instructions carefully and apply the coating evenly.
How do you clean rusty quarters?
If you have a collection of quarters that are tarnished, you may be wondering how to clean them without damaging the metal.
Fortunately, there are several safe and effective methods you can use to restore your coins to their original shine.
Vinegar
One popular method for cleaning rusty quarters is to soak them in vinegar. Fill a bowl with white vinegar and place your coins in the bowl for a few minutes.
Then, use a toothbrush to gently scrub the coins, careful not to scratch the surface. Finally, rinse the coins with water and dry them with a soft cloth.
Baking soda
Another effective method for cleaning rusty quarters is to make a paste of baking soda and water.
Apply the paste to the coins and rub them gently with a cloth or toothbrush. Then, rinse the coins with water and dry them with a soft cloth.
Mineral oil
If you prefer a gentler method, you can try rubbing your rusty quarters with mineral oil.
Simply apply a small amount of oil to a soft cloth or cotton swab and rub the coins gently.
This method is especially effective for removing light tarnishes.
Warnings
When cleaning rusty quarters, it’s important to avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasives that can damage the metal.
You should also avoid scratching or scraping the surface of the coins, as this can cause further damage. Finally, do not boil or heat the coins, which can damage the metal.
Following these simple tips, you can safely and effectively clean your rusty quarters and restore them to their original shine.
Do quarters have metal in them?
Of course, quarters have metal in them! Quarters are made of a copper-nickel alloy. The first quarters were minted in 1796 and were made of pure silver.
However, the current quarters were introduced in 1965 and are made of 91.67% copper and 8.33% nickel. This composition provides the coin with a distinct appearance and also helps to prevent rusting.
The weight and diameter of a quarter are 5.67 grams and 24.26 millimeters, respectively. The coin features a portrait of George Washington on the obverse side and an eagle on the reverse side.
It is a common misconception that quarters are made of silver.
While some older quarters may contain silver, the modern-day quarters are primarily made of copper and nickel.
This composition ensures that the coin is durable and long-lasting.
The copper-nickel alloy used in quarters is resistant to corrosion and tarnishing. This means that quarters do not rust.
Overall, quarters are a staple of American currency and are made of a durable copper-nickel alloy that ensures longevity.
Can Rusty Quarter Be Worth Anything?
You may be wondering if a rusty quarter can be worth anything. The answer is that it depends on the condition and rarity of the quarter.
Corrosion or tarnish can affect the value of a quarter, so it’s important to consider this when evaluating a coin.
A lightly corroded or tarnished quarter may still be worth its face value or slightly more if it is rare or collectible.
However, a heavily corroded or tarnished quarter may be worth less than its face value or nothing if it is common or damaged.
It’s important to note that the value of a coin is not solely determined by its condition but also by its rarity and historical significance.
If you have a corroded or tarnished quarter, it’s crucial to determine its rarity and historical significance before evaluating its value.
Some quarters may be worth more than their face value if they are error coins or have unusual features.
For example, a 1955 doubled die quarter may be worth thousands of dollars, even if heavily corroded or tarnished.
In conclusion, the value of a rusty quarter depends on its condition, rarity, and historical significance. It’s important to evaluate these factors before determining the value of a coin.
Sharing is caring!